Last updated on: September 6, 2025
If you’ve ever visited a construction site, you’ll know one thing for sure—reinforcement steel (rebars) are the backbone of concrete structures. Whether it’s a small residential slab or a multi-story building, reinforcing steel ensures strength, safety, and durability.
But here’s the problem: It’s not always easy to calculate the right size, quantity, and weight of reinforcing steel. The reinforcing steel calculator, or rebar weight calculator, proved to be helpful in the same place. It helps engineers, contractors, and even students to save time, reduce errors, and ensure accuracy.
This calculator guide will explain everything to you, from understanding reinforcing steel sizes to using calculators on-site like an expert.
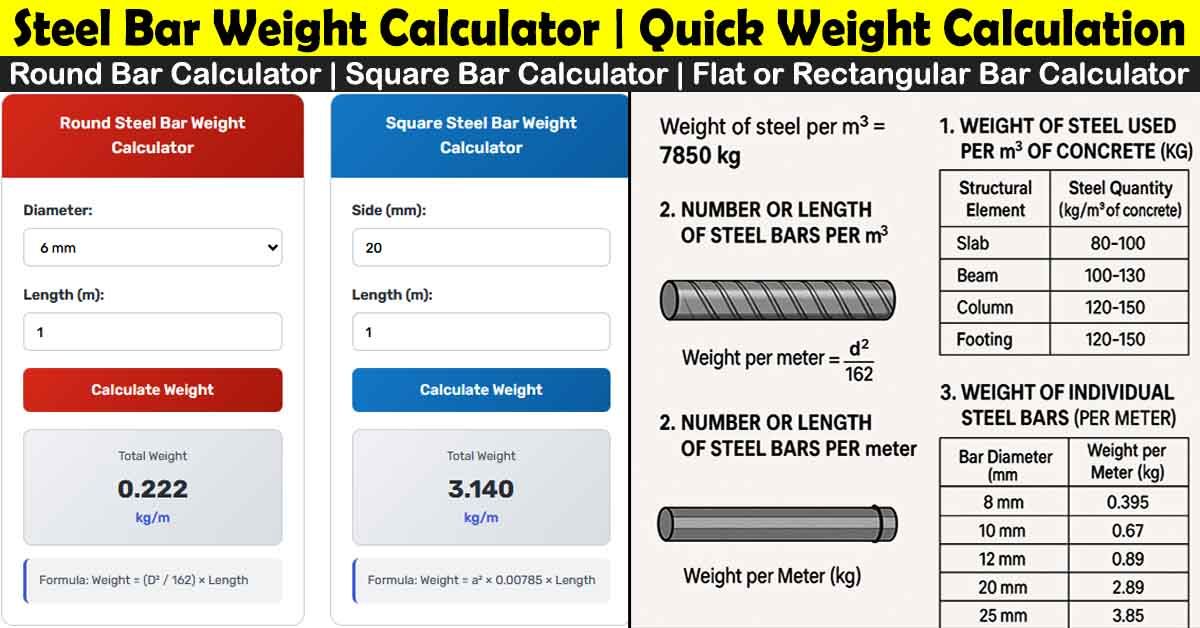
Reinforcing Steel Calculator
Formula:
Weight = (D² / 162) × Length × Number of Bars
* Calculation uses: Total Weight = Unit weight of bar × Length × Number of bars
Unit Weight:
Total Weight:
Unit Weight – Weight in Kg/m
| Diameter (mm) | Unit Weight |
|---|
What is a Reinforcing Steel Calculator?
The Reinforcing Steel Calculator is a simple yet powerful tool that helps you find out:
- Weight of steel bars based on diameter and length
- Cross-sectional area of reinforcing steel
- Steel bar quantity required for construction projects
- Comparison between different reinforcing steel sizes
Instead of memorizing the formula or looking at the chart, you just insert a few values, and the calculator calculates automatically. This calculator tells you the exact amount of rebar required, including reinforcing steel sizes and reinforcing steel weight.
Why Is Reinforcing Steel Calculation Important?
Reinforcing steel isn’t just a common building material—it’s a protective element. The results of incorrect calculations can be:
- Overestimation: The cost of steel and the project budget are increasing.
- Underestimating → Leads to weak structures and potential failures.
The use of a reinforcing steel weight calculator is ensured:
- Design accuracy (as per ACI, Eurocode, BS or ASTM codes)
- Reduction in construction costs
- Safe and durable structures
Steel gives strength, but precision gives trust — calculate wisely, build forever.
Basic Formula Behind Reinforcing Steel Weight
Before calculators existed, engineers used the standard formulas:
Weight of Steel Formula (Kg/m):
Weight of Steel (kg/m) = W = (d² ÷ 162) X L
Where:
- d = Diameter of bar (in mm)
- L = Length of Bar (in m)
- W = Weight of Bar (in Kg)
Example:
For a 16 mm bar having a length of 7 m, → Weight = (16² ÷ 162) x 7 = 1.58 x 7
Total Weight = 11.06 Kg
This formula is built into most calculators, making life much easier for engineers and site supervisors.
Weight of Steel Formula (Kg/ft):
Weight of Steel (kg/m) formula = W = (d² ÷ 533) X L
Where:
- d = Diameter of bar (in mm)
- L = Length of Bar (in m)
- W = Weight of Bar (in Kg)
Example:
For an 8 mm bar having a length of 6 ft, → Weight = (8² ÷ 533) x 6 = 0.120 x 6
Total Weight = 0.720 Kg
Weight of Steel Formula (Lb/ft):
Weight of Steel (kg/m) formula = W = (d² ÷ 24) X L
Where:
- d = Diameter of bar (in # number)
- L = Length of Bar (in m)
- W = Weight of Bar (in Kg)
Example:
For a #5 bar having a length of 5 ft, → Weight = (5² ÷ 24) x 5 = 1.042 x 5
Total Weight = 5.208 Lbs
Reinforcing Steel Sizes and Charts
A standard reinforcing steel chart is your quick-reference guide. It saves you from calculating the weight for every single bar size every time. A good chart includes:
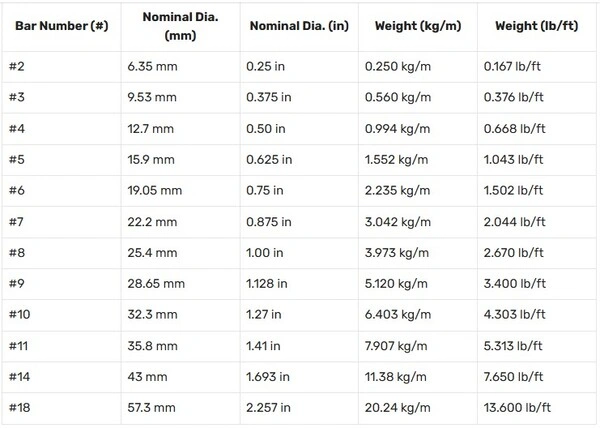
Steel Rebar Sizes in mM with Area and Weight for Rebar Calculator:
| Dia (mm) | Area (mm²) | Weight (kg/m) | Weight (kg/ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 28.274 | 0.222 | 0.0677 |
| 8 | 50.265 | 0.395 | 0.1203 |
| 10 | 78.540 | 0.617 | 0.1879 |
| 12 | 113.097 | 0.888 | 0.2706 |
| 16 | 201.062 | 1.578 | 0.4811 |
| 20 | 314.159 | 2.466 | 0.7517 |
| 25 | 490.874 | 3.853 | 1.1745 |
| 28 | 615.752 | 4.834 | 1.4733 |
| 32 | 804.248 | 6.313 | 1.9243 |
| 36 | 1017.876 | 7.990 | 2.4355 |
| 40 | 1256.637 | 9.865 | 3.0067 |
| 50 | 1963.495 | 15.413 | 4.6980 |
Real-World Applications of Reinforcing Steel Calculators
Site Engineers
- Bar banding schedule (BBS) calculations.
- Estimating the amount of rebar during concreting.
Contractors
- Budget planning for steel purchases.
- Avoid buying more or less than you need.
Students and trainee engineers
- Learning the effects of different steel sizes.
- Practical calculations without complex charts.
Structural designers
- Reinforcement confirmation in beam, column, and slab.
- Ensuring the design is according to engineering codes.
Common Mistakes Engineers Make (and How Calculators Help)
- Manual calculation errors → Calculator uses automatic formulas.
- Don’t add waste calculations → Calculators can add a 3-5% increase.
- Incorrect bar size estimation → Calculator confirms according to the chart.
- Relying on the rules of thumb → Calculators calculate according to the correct standard.
Pro-tip for students: Always check the results of the calculator from theoretically. This will strengthen your understanding.
Tips for Civil Engineering Students and Professionals
- Learn both hands-on (manual) and digital methods → A calculator is a tool, but theory is the foundation.
- Use reinforcing steel calculators during internship → This will affect supervisors.
- Practice Bar Banding Schedule (BBS) → Essential in both exams and on-site.
- Keep the Reinforcing Steel Chart to yourself → Instantly helps to understand size.
Industry Standards & Codes for Reinforcing Steel
Most reinforcing steel calculators are designed to work in compliance with these standards.
- ASTM A615 / A706 – U.S. reinforcing bar standards
- BS 4449 – British Standard for steel reinforcement
- IS 1786 – Indian Standard for high-strength deformed bars
- ACI 318 – Structural Concrete Design Code
Conclusion
The reinforcing steel calculator is a must-have tool for anyone who works with concrete and rebar. It simplifies the estimates in choosing reinforcing steel sizes, calculating the reinforcing steel area, and knowing the reinforcing steel weight. By using this tool, you save time. Save, spend less money, and make your project safer and stronger. Whether you’re looking at a reinforcing steel size chart or learning how to tie reinforcing steel, this calculator makes the work easier and faster. Try it out today to make your construction project stronger. Be easy and get professional results!
FAQs
Answering Your Burning Questions on Reinforcing Steel Calculators
Q1: What is a reinforcing steel calculator used for?
This calculator is used to calculate the quantity, weight, and size of steel used in concrete structures so that the plan can be easily made and the cost can be estimated.
Q2. How do I calculate rebar manually?
Use the formula W=d2/162 for round bars, where d is the diameter in mm.
Q3: How are reinforcing steel sizes indicated?
The sizes are usually specified by diameter in millimeters or American numbering (such as #3, #4, etc.) which indicate the size and weight of the ba
Q4: What standards do reinforcing steel calculators follow?
It generally follows standards such as ASTM A615, BS4449, and GB1499.2-2007 so that the results are in accordance with construction rules.
Q5: How do I tie reinforcing steel correctly
The CRSI and other organizations have advised using tying techniques like the figure-eight tie, wrap-and-snip tie, and snap tie.
Q6: Are there weight charts available for reinforcing steel?
Yes, weight charts show the weight per meter for different bar diameters, which is necessary for calculations in the calculator.